Tableau Session 01: Introduction To Tableau
Workbooks, Data Types, Fields, Basic Charts, Filtering
Introduction to Tableau
This chapter sets the foundation for working with Tableau — from connecting to data, through building your first visuals, to publishing a simple dashboard.
You’ll learn core concepts (dimensions, measures, discrete/continuous), get oriented in the interface, and apply best practices while creating your first views.
By the end of the class, you should be able to connect to common data sources, explain Tableau’s core data concepts, and publish a simple, well-structured dashboard with basic interactivity.
What Is Tableau?
Tableau is a visual analytics platform that turns data into insight through interactive charts and dashboards.
In practice, Tableau bridges raw tables and business understanding, enabling you to explore, explain, and share findings quickly.
The typical Tableau workflow follows five stages:
- Connect – link to files (Excel/CSV), databases, or cloud sources.
- Prepare – profile fields, set data types, create relationships/joins, and fix quality issues.
- Visualize – build views on shelves with Marks (color/size/label/shape).
- Compose – assemble sheets in dashboards; add filters, actions, and layout.
- Publish & Share – deliver to Tableau Public, Cloud, or Server for feedback and decision-making.
This flow is iterative: each visualization raises new questions — adjust, test, and refine.
Business Applications of Tableau
Tableau supports decision-making across multiple industries:
- Telecommunications: network KPIs, churn monitoring, device mix, and customer segmentation.
- Retail & E-commerce: category performance, retention cohorts, and funnel analysis.
- Finance: credit risk dashboards, revenue tracking, portfolio monitoring.
- Marketing: campaign attribution, A/B test results, and media mix performance.
- Healthcare & Public Sector: patient outcomes, resource management, and geographic analytics.
Unifying theme: Tableau accelerates how analysts move from questions → visuals → decisions.
Tableau Products
| Product | Description |
|---|---|
| Tableau Desktop | The primary tool for creating visualizations and dashboards. |
| Tableau Prep | A data preparation tool for cleaning and reshaping data before visualization. |
| Tableau Server | On-premises platform for sharing dashboards securely within organizations. |
| Tableau Cloud | Cloud-based alternative for publishing and managing dashboards without server setup. |
| Tableau Public | Free, web-based platform for publishing dashboards publicly. |
| Tableau Next | A new feature for automated insight generation and trend detection. |
Download: Tableau Public
Sample Datasets: Sample Data
Dataset used: airbnb.xlsx

Tableau File Types
| File Type | Extension | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Workbook | .twb |
Contains worksheets, dashboards, and connections (without data). |
| Packaged Workbook | .twbx |
Workbook + embedded data and images (portable). |
| Data Source | .tds |
Contains metadata and field properties. |
| Packaged Data Source | .tdsx |
Data source + data extract (portable). |
| Extract | .hyper |
Optimized extract of data for faster performance. |
| Bookmark | .tbm |
Saves a single worksheet for reuse. |
Data Types in Tableau
| Type | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Number (Decimal) | Price |
Quantitative data with decimals. |
| Number (Whole) | Host ID |
Integer data without decimals. |
| Date / Date & Time | Host Since |
Temporal data. |
| String | Property Type |
Textual or categorical values. |
| Geographic Role | Zip Code |
Fields that can be mapped geographically. |
| Boolean | True/False |
Logical values used in filters or calculations. |
Dimensions vs. Measures
- Dimensions contain qualitative fields (categories such as names, dates, or geographic data).
→ Used to group, filter, and categorize data.
- Measures contain quantitative, numeric fields.
→ Used to aggregate and analyze data (SUM, AVG, COUNT).
Discrete vs. Continuous Fields
| Concept | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Discrete | Distinct categories, shown as separate labels or headers. | Customer Name, Region |
| Continuous | Numeric or time fields forming an unbroken scale. | SUM(Sales), Order Date |
Tip: You can convert measures or dimensions between discrete and continuous using the field dropdown.
 |
 |
|---|---|
| Continuous | Discrete |
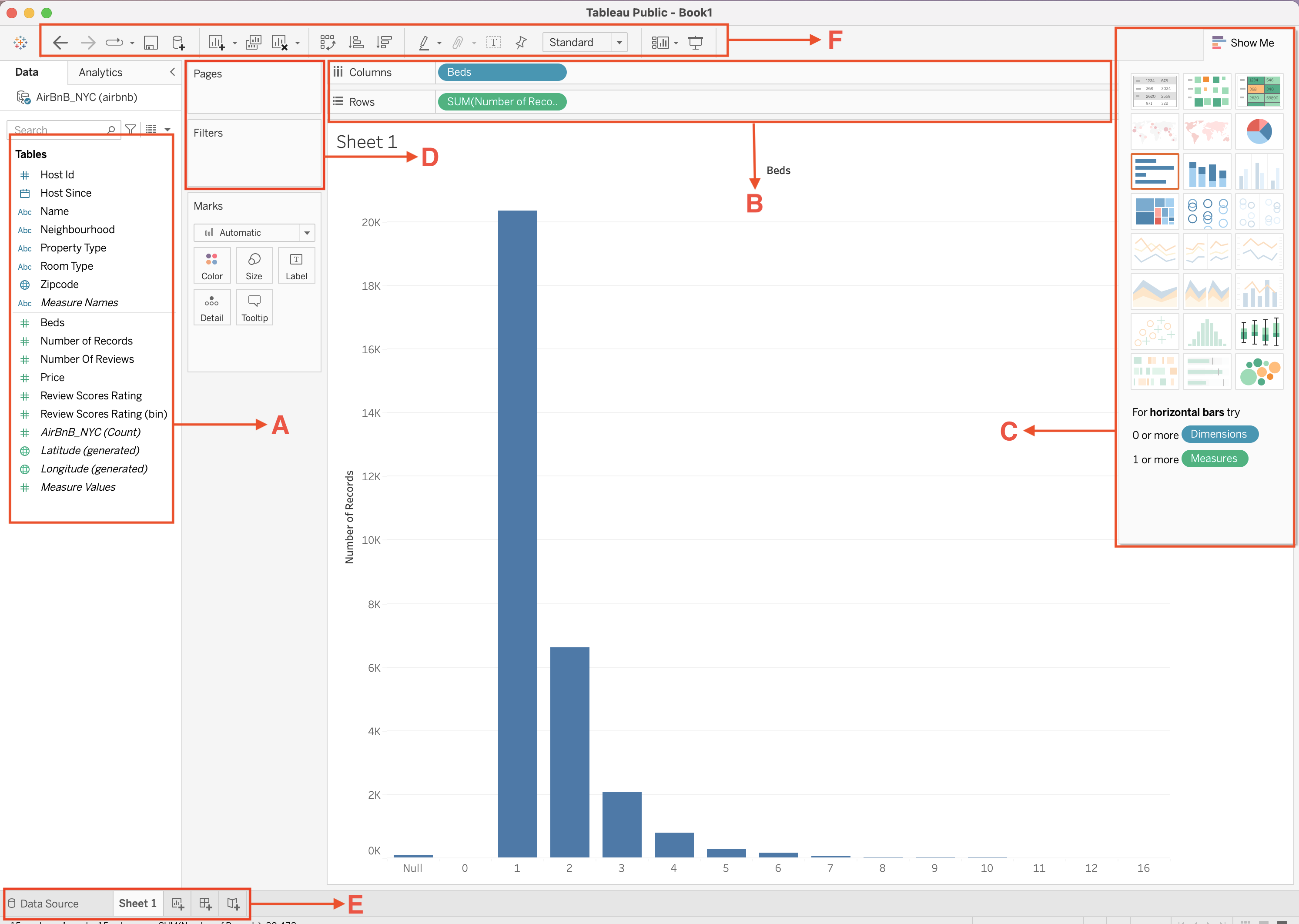
Tableau Interface Overview
| Section | Function |
|---|---|
| A. Data Pane | Contains all fields (dimensions, measures, parameters). |
| B. Shelves | Control how fields appear in the view (Rows, Columns, Filters). |
| C. Marks Card | Controls visual elements (Color, Size, Label, Shape, Tooltip). |
| D. Filters Shelf | Limits the data shown in the visualization. |
| E. Dashboard Pane | Combines multiple sheets into a single interactive view. |
| F. Toolbar & Buttons | Quick access to tools (undo, redo, sort, swap, etc.). |
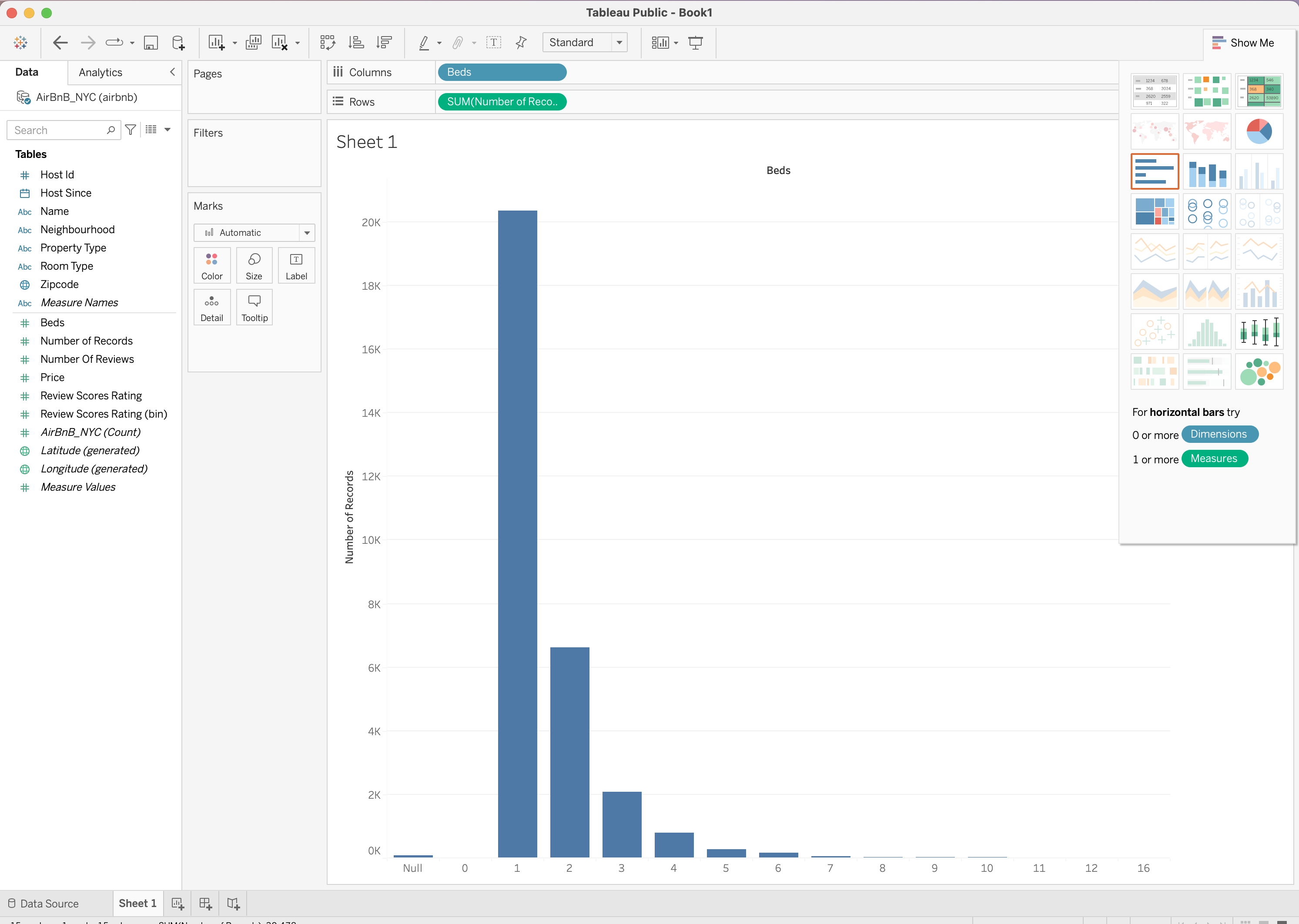
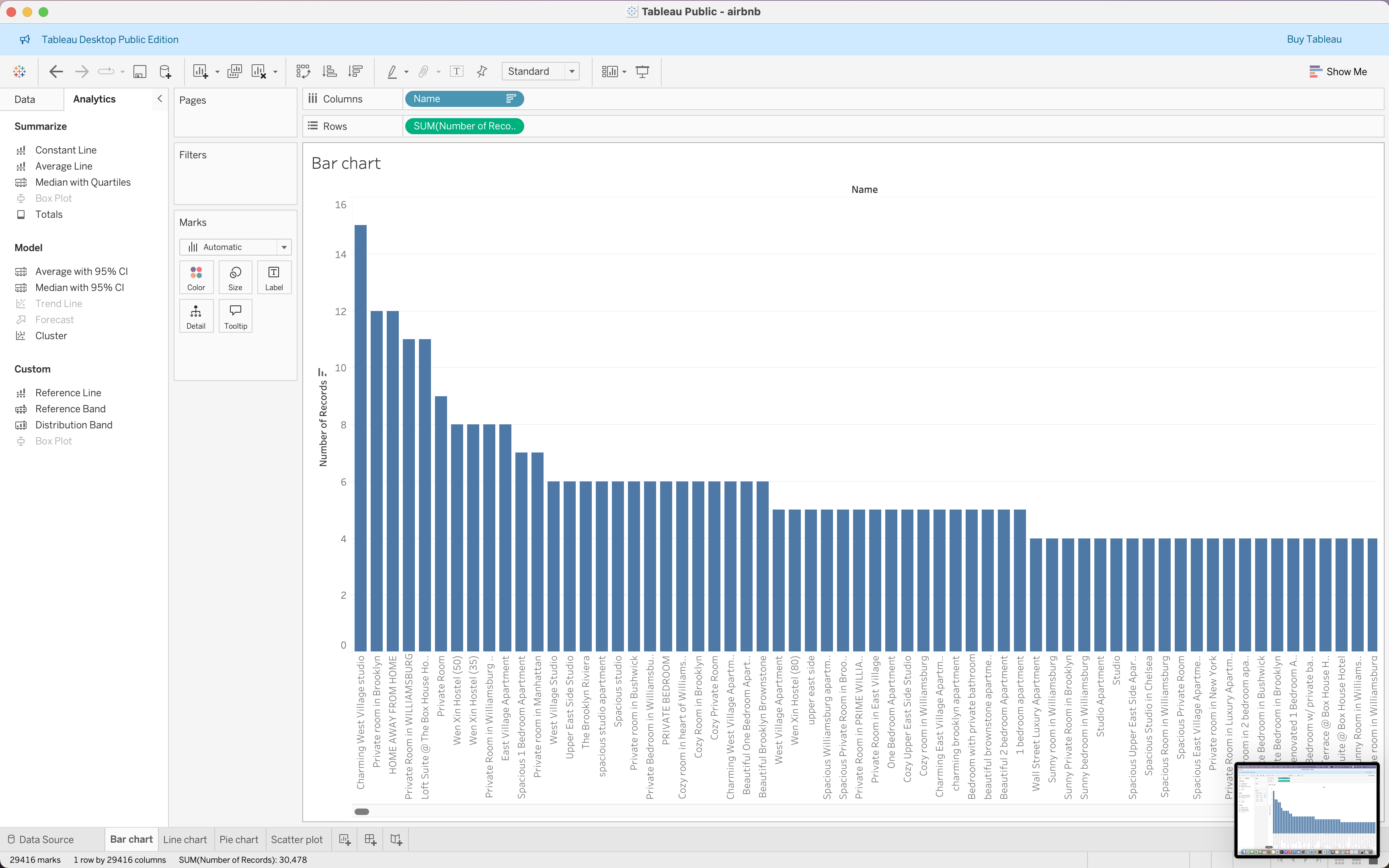
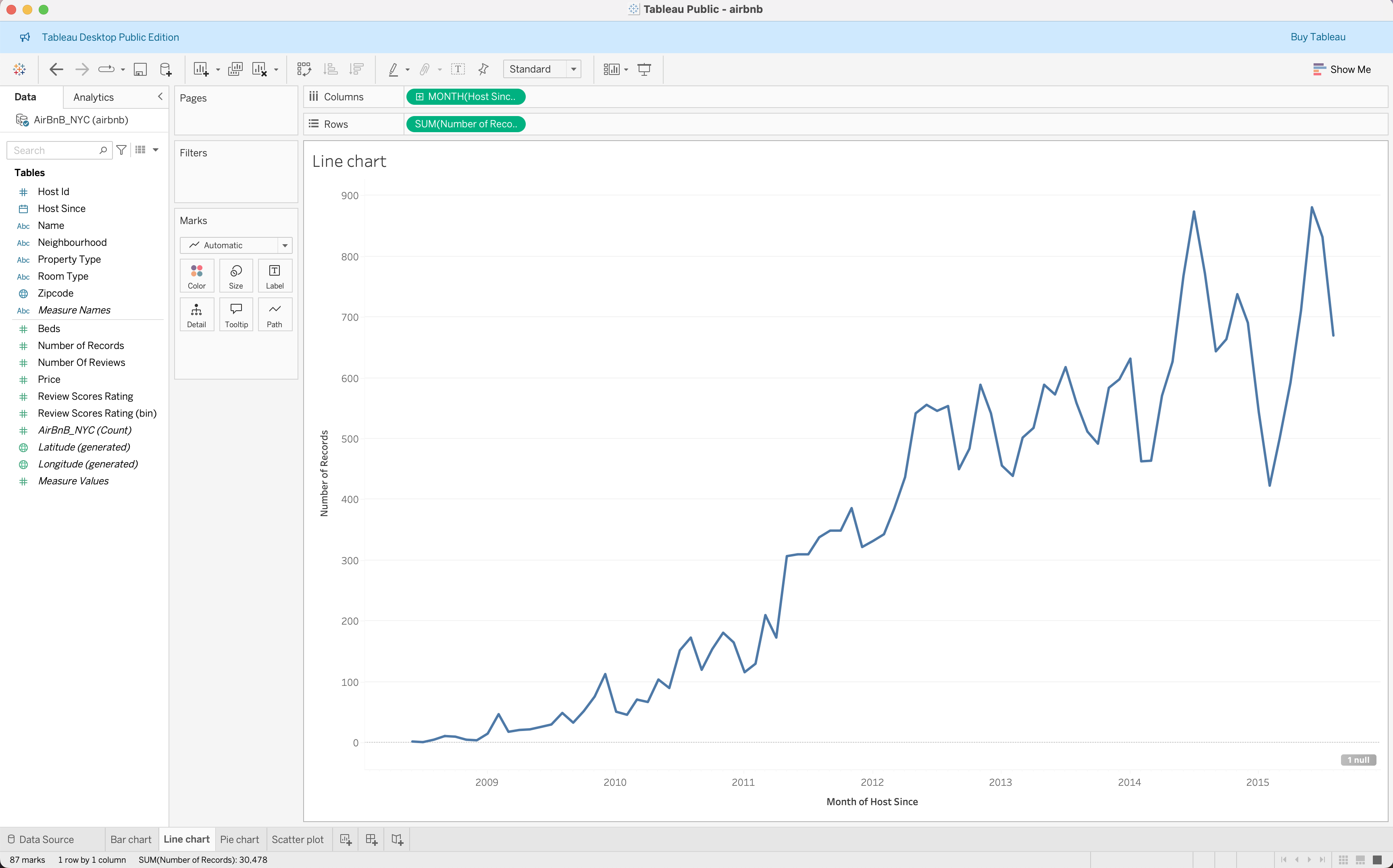
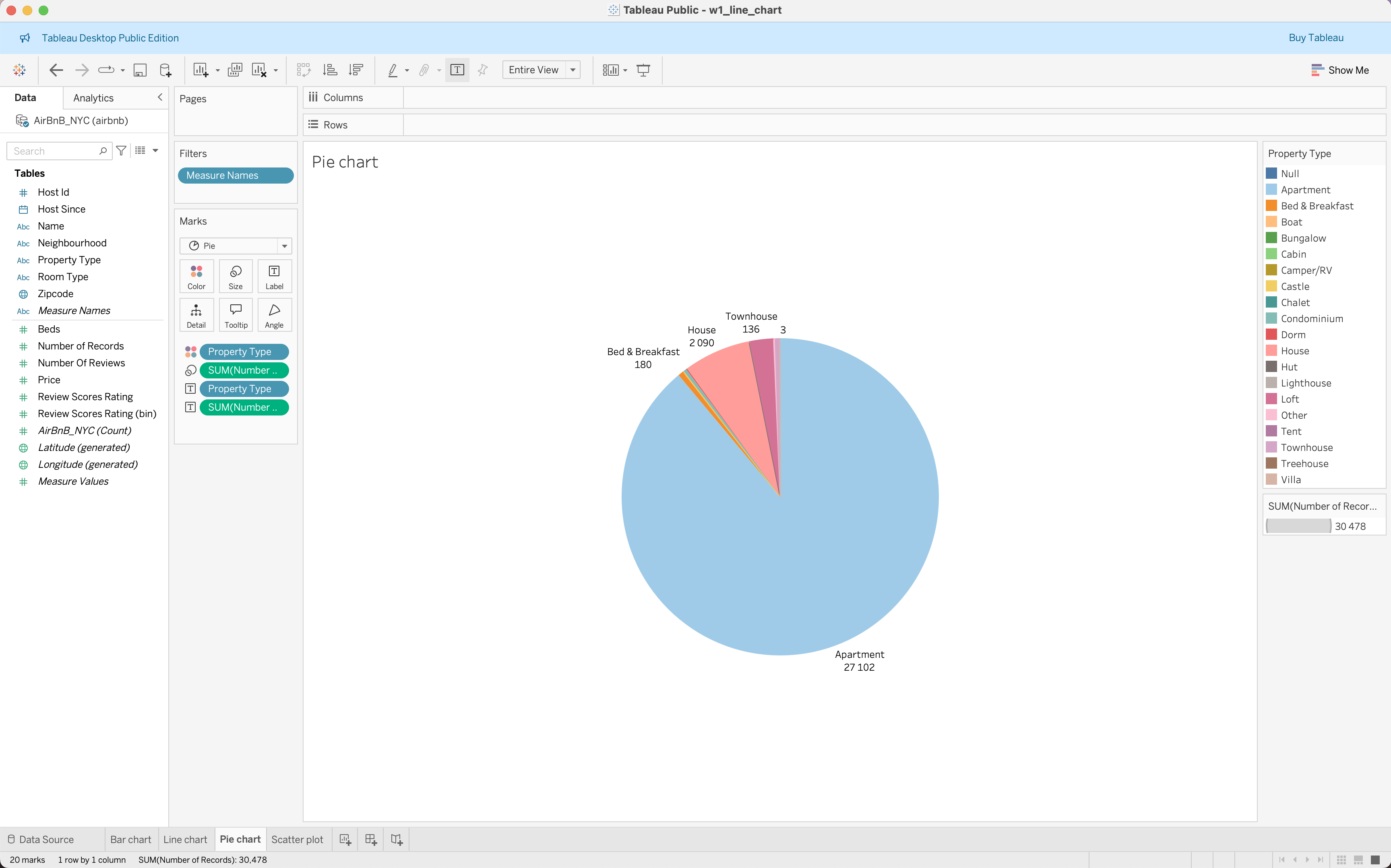
Creating Basic Charts
 |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bar Chart | Line Chart | Pie Chart | Scatter Plot |
Filters, Groups, Sets, and Sorting
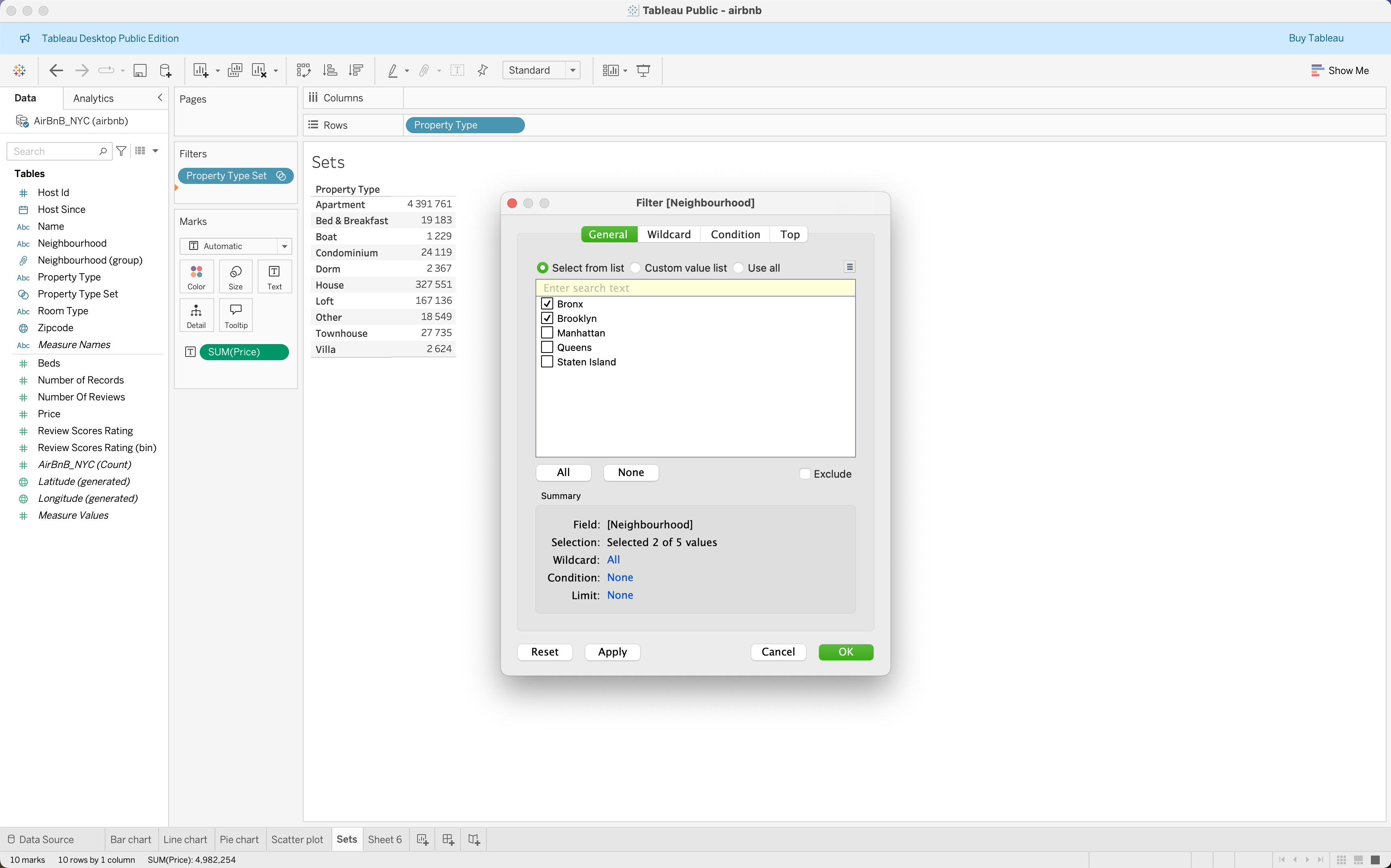 |
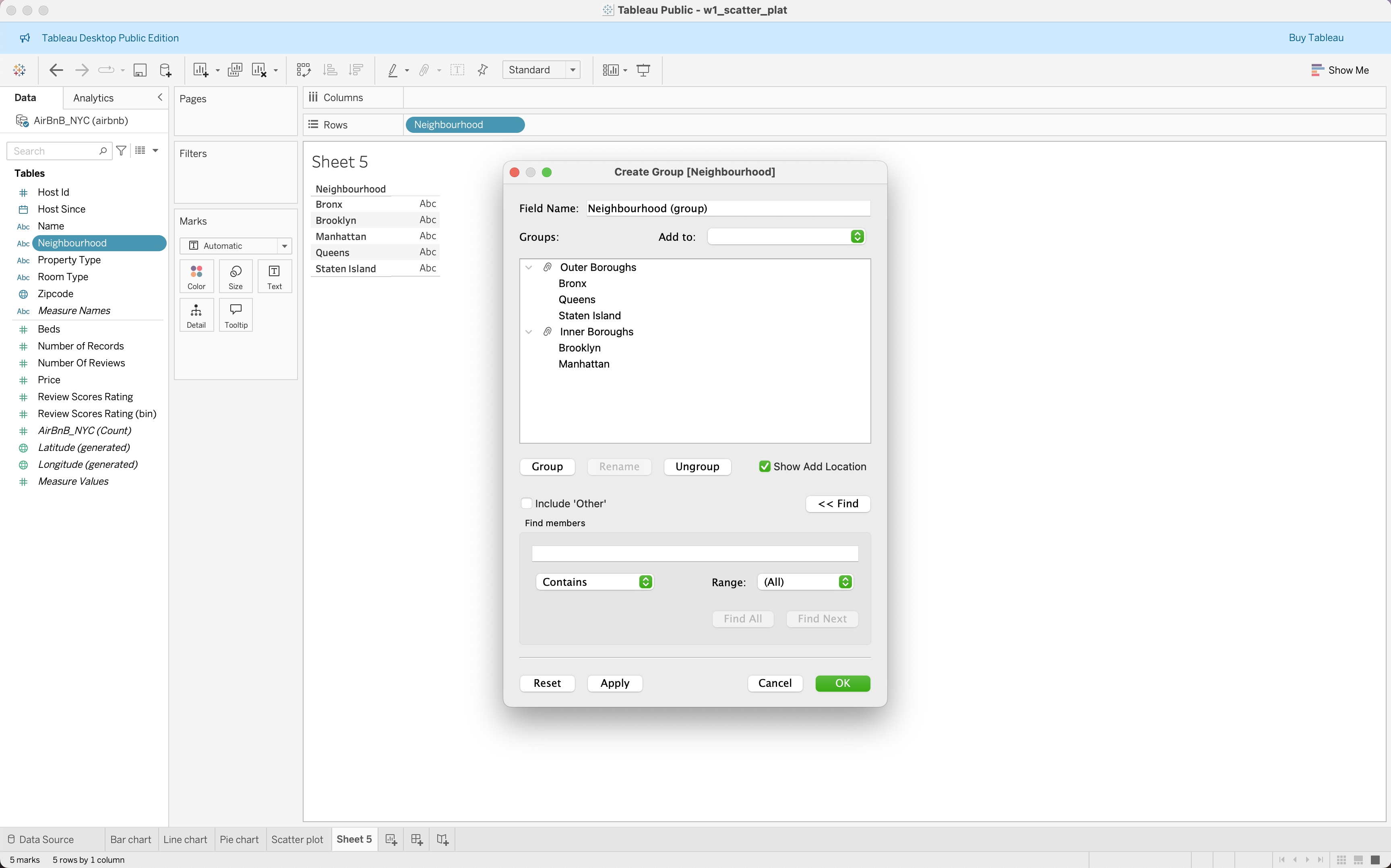 |
 |
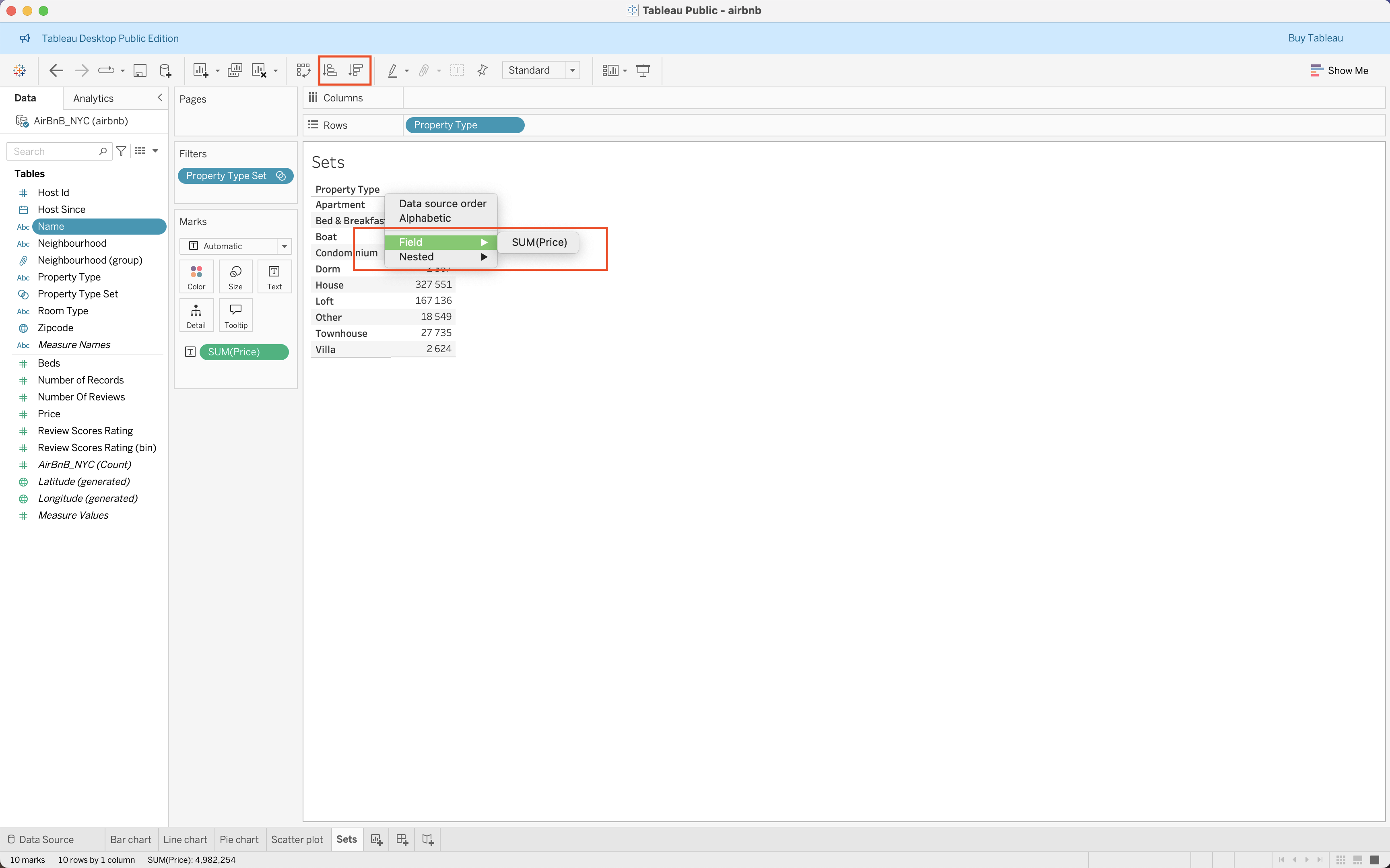 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Filters | Groups | Sets | Sorting |
Assignment
Create a simple Tableau dashboard using the Airbnb dataset.
- Connect to
airbnb.xlsx
- Build at least three visualizations (bar, line, scatter, or pie)
- Add a filter or group for interactivity
- Publish your dashboard to Tableau Public
- Include a short reflection (2–3 sentences) on what your visualization shows.
Recommended Resources
Articles 1. Getting Started with Tableau
2. Chart Chooser for Tableau
Videos 1. Introduction to Tableau for Beginners